Page content
CLP Hazard Icon Meaning
Hazardous substances are provided with pictograms that provide information about the (health) risks to people and the environment. The criteria for this classification are described in the Globally Harmonized System of Classification and Labeling of Chemicals (GHS-CLP) of the United Nations. In 2023, revision 10 was published.
Explosive (GHS01)
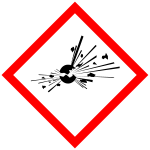
Unstable substances and preparations that can explode are marked with this symbol. Examples are fireworks and ammunition, picric acid.
Flammable (GHS02)
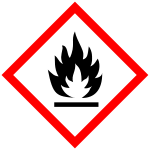
Flammable gases, vapors or liquids are marked with this symbol. Examples are alcohols, hydrocarbons (petrol).
Oxidizing (GHS03)
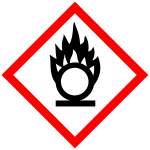
These are gases, substances and mixtures that can cause or promote fire with other substances. Examples are oxygen, bleach.
Pressurized gases (GHS04)
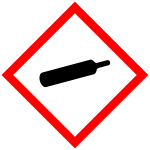
This group includes compressed gas (pressure containers), liquefied gases, highly cooled liquefied gases and dissolved gases. Examples are gas cylinders and aerosols.
Corrosive (GHS05)
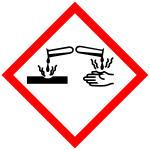
This group includes substances that are corrosive to metals, to the skin and that can cause serious eye damage. Examples are acetic acid, hydrochloric acid, ammonia.
Toxic (GHS06)
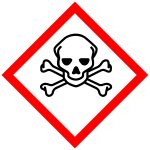
Substances and mixtures that, if inhaled or absorbed through the mouth or skin, can cause harmful effects or even death almost immediately. Examples are pesticides, methanol.
Irritant, sensitizing, harmful (GHS07)
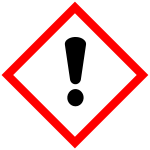
These are substances or mixtures that are irritating in direct, prolonged or repeated contact with the skin or mucous membranes. This group also includes substances that can cause dizziness or an allergic skin reaction. Examples are detergents, SDS, 2-mercaptoethanol.
Long-term health hazard (GHS08)
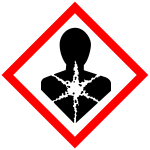
This includes carcinogenic, mutagenic and reprotoxic substances (CMR substances). This group includes substances that cause asthma symptoms when inhaled, substances that can be fatal if ingested and substances with specific target organ toxicity (STOT). Examples are lamp oil, turpentine, acrylamide.
Hazardous to the aquatic environment (GHS09)
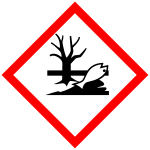
Substances which, when discharged into the environment, are toxic to aquatic life, sometimes with long-lasting effects. Examples are pesticides, biocides.
