Page content
- Section 1: Identification of the substances or mixture and the company
- Section 2: Hazard identification
- Section 3: Composition and information on ingredients
- Section 4: First aid measures
- Section 5: Fire-fighting measures
- Section 6: Accidental release measures
- Section 7: Handling and storage
- Section 8: Exposure control measures/personal protection
- Section 9: Physical and chemical properties
- Section 10: Stability and reactivity
- Section 11: Toxicological information
- Section 12: Ecological information
- Section 13: Disposal Instructions
- Section 14: Information relating to transport
- Section 15: Regulatory
- Section 16: Other information
The Dutch abbreviation VIB (veiligheidsinformatieblad) means safety data sheet. SDS is the English name for a safety data sheet. With the introduction of the European regulation REACH (Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemical Substances), the abbreviation SDS is used. An SDS has a fixed structure and consists of 16 sections and 46 subsections. They are below the image.
The supplier of a hazardous substance is obliged to provide an SDS with a first delivery. If the supplier adjusts the SDS, he must send an adjusted SDS with the next order. If you want to have an SDS again later, you can always request it from the supplier. Suppliers often have a website with safety information about their products.
The umcs have their own database of SDS with more than 5000 substances. The Safety Data Sheets (SDS) and Workplace Instruction Cards (WIK) in the NFU Database have been validated; This means that the accuracy and topicality of the content has been checked. The database can be accessed via intranet in every umc. No login code or password is required for this.
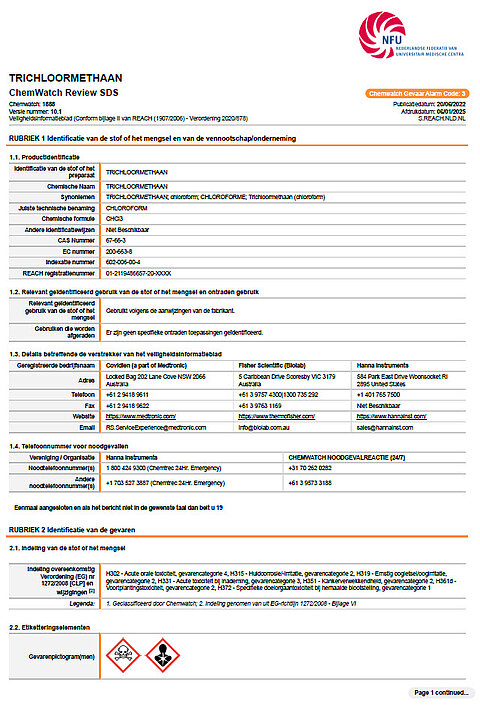
Below is the first page of the safety data sheet on chloroform as an example.
Section 1: Identification of the substances or mixture and the company
1.1 Product Identification
The name used must be the same as the name on the label and in accordance with Annex VI of Directive 67/548/EEC or Regulation EC No 1272/2008.
1.2 Relevant identified uses of the substance or mixture
This states, as far as is known, what the substance or preparation is used for. Furthermore, it is briefly described what the substance or mixture actually does, for example a fire retardant or an antioxidant.
1.3 Details of the provider of the safety data sheet
It shows the identity of the person responsible for placing the substance or mixture on the market in the European Community. This is the manufacturer, the importer or the distributor. It also contains the full address, telephone number and e-mail address of the authorized person responsible for the safety data sheet.
1.4 Emergency Phone Number
In case of emergency, this telephone number of the company and/or the competent official advisory body can be used.
Section 2: Hazard identification
Section 2 lists the hazards of the substance or preparation
2.1 Classification of the substance or mixture
Here are the H-phrases according to the classification according to Regulation (EC) No 1272/2008 [CLP] and amendments.
2.2 Label elements
Here are the hazard pictogram(s), the signal word and the H and P phrases that appear on the label.
2.3 Other hazards
This may contain additional information regarding the substance or mixture.
Section 3: Composition and information on ingredients
This section lists the hazards of the individual constituents of the substance or preparation. This is in a tabular form with the ingredients, the amount (in % or concentration), the CAS number and the H-phrases.
Section 4: First aid measures
The first aid measures are described here. If immediate medical attention is required, this is at the top. The information is broken down into different headings according to the different routes of exposure:
- Eye contact
- contact with the skin
- swallow
- Inhale
Section 5: Fire-fighting measures
Reference is made here to the instructions for fighting a fire caused by, or in the vicinity of, the substance or preparation. This section also includes:
- the suitable extinguishing media
- the extinguishing media that may not be used for safety reasons
- special exposure hazards caused by the substance or preparation itself, combustion products or released gases
- special protective equipment for firefighters
Section 6: Accidental release measures
This section contains the (precautionary) measures in case the substance or preparation is accidentally released. How can you protect yourself, how should you collect, neutralize or absorb the product and how do you protect the environment?
Section 7: Handling and storage
Here are the recommendations for safe handling, storage and use for people and the environment. What technical measures are needed, such as local or general ventilation. How can you prevent aerosol, dust formation and fire.
This section also states whether you need to store the product separately from other substances.
Section 8: Exposure control measures/personal protection
8.1 Control Parameters / Exposure Limits
Here are the limit values for occupational exposure. These values apply to the Member State where the substance or preparation is placed on the market.
8.2 Exposure control measures
This section explains the measures you need to take to control exposure to people and the environment.
How do you protect the respiratory system? Which types of gloves are suitable with which breakdown time? What type of eye protection do you use and are there any other specific hygiene measures needed?
Section 9: Physical and chemical properties
Here you will find all the relevant physical and chemical properties of the substance or preparation.
General information
Appearance, color, solid, liquid or gas and smell.
Physical properties
- Boiling point or boiling range
- Flash point
- flammability (solid, gas)
- Explosion hazard, explosion limits
- Oxidizing properties
- vapour pressure
- Relative density
- solubility
- Water solubility
- vapor density
- Evaporation rate
Section 10: Stability and reactivity
This states whether the substance is stable, with which substances the product can react dangerously and whether the decomposition products can pose a danger to people or the environment.
Section 11: Toxicological information
Here you can find toxicological information. Which health effects occur acutely after exposure (sensitization, drowsiness). What effects can occur in the longer term (CMR effects, cancer, fertility). This section also contains the LD50 or LC50 for gases.
Section 12: Ecological information
The possible effects if the substance ends up in the environment are described here. What aquatic effects can be expected, can the substance end up in the groundwater or in the food chain and is the substance biodegradable or not?
Section 13: Disposal Instructions
How can you dispose of the product, its residue or waste safely for people and the environment? If removal poses a danger, what measures should you take? Which method is appropriate for disposal: incineration, recycling, landfill, etc.
Section 14: Information relating to transport
This section states whether the transport of dangerous goods is subject to ADR (land transport), IMDG (sea), RID (rail), ICAO/IATA (air). Here you can find relevant information about, among other things:
- UN number
- class
- labelling
- Packaging group
Section 15: Regulatory
This section contains other information about the substance or mixture that is not already included in the safety data sheet:
- whether a substance is included in the SZ list CMR substances
- whether a substance is included in other lists, such as a list of limit values, prohibited substances, etc.